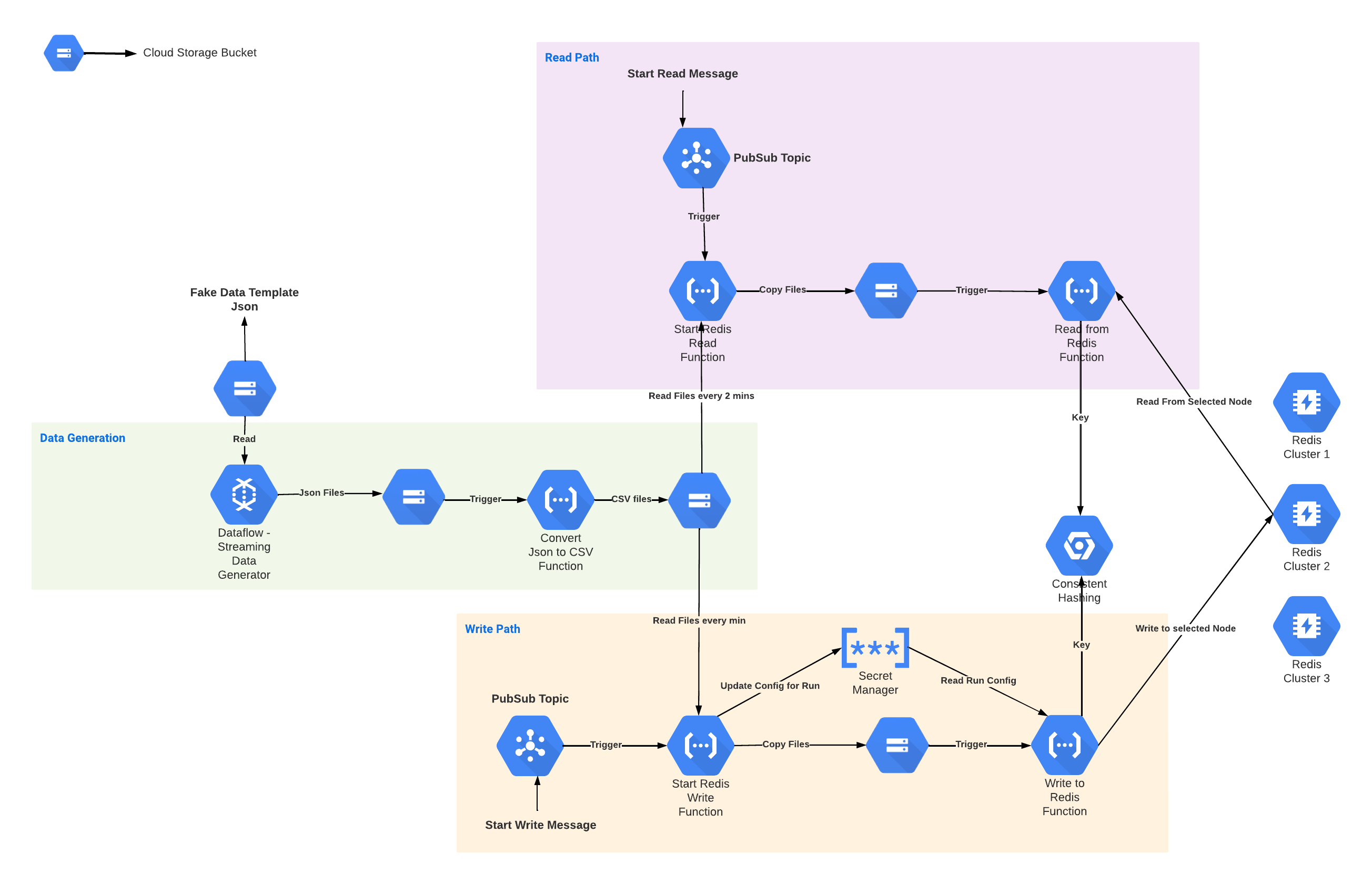
This is WIP framework to load test redis cluster(s). The idea is to have an end to end setup that allows configurable load going to either a single or multiple Redis Clusters.
Performance of applications and services are highly dependent on the data being used. One will get different set of performance numbers if KBs of data is being used versus MBs of data.
There are hardcoded paths and strings in this code base atm - it will be removed in later cleanup cycles.
This framework uses Dataflow Streaming Data Generator Template to generate fake data for performance tests. Once we have fake data,
in the examples included, we convert this JSON data to CSV - this step is completely optional and one could work with JSON files directly.
We control Writing to and Reading from Redis via Pub/Sub. We publish below messages for starting the write and read flows.
Begin Write:
start-mme:run-0504-1040:10.40.208.21:10000:60:mme_csv:mme_minute_dropzone:60
This start write message to pubsub is then parsed by the start-write cloud function as below:
tokens = message.split(":")
if(tokens[0] != "start-mme"):
return
run_id = tokens[1]
redis_ip = tokens[2]
chunk_size = tokens[3]
max_threads = tokens[4]
source = tokens[5]
destination = tokens[6]
files_to_copy = int(tokens[7])
where,
redis_ip = not in use
chunk_size= size in which to divide a file into
max_threads = number of parallel threads readind file chunks and uploading data to Redis
source = source gcs bucket to read data files from
destination = destination gcs bucket to write files to at a given frequency
files_to_copy = number of files to copy every min (hard coded for now)
Begin Read:
start-ipfr:run-0504-0803:mme_csv:fake_ipfr:75
This start read message to pubsub is then parsed by the start-read cloud function as below:
tokens = message.split(":")
if(tokens[0] != "start-ipfr"):
return
run_id = tokens[1]
source = tokens[2]
destination = tokens[3]
files_to_copy = int(tokens[4])
where,
source = source gcs bucket to read data files from
destination = destination gcs bucket to write files to at a given frequency
files_to_copy = number of files to copy every 2 mins (hard coded for now)
Important to note that the chunk_size and max_threads is not currently passed to read flow and are hardcoded in the read-mme-redis cloud fucntion.
We use a unique run-id for each performance test to identify metrics for that run and also to copy the same set of files with different names to avoid
creating new files for each run.
The strat-write function writes part of the config it received from pubsub message to a secret manager key. This is key is then read by subsequent function that actually reads N files per min and writes to Redis.
This framework uses ZADD i.e. Sorted Set writes and ZREVRANGE for reads. In future, the framework would make that configurable as well. In the example data used for performance tests - a total of max 100 bytes of data is sent/read from redis for each record in a file.
A few things to note
- processing all files in a process does not scale
- processing a file line by line does not scale
- processing a file in a single thread does not scale
- writing or reading records/keys one at a time from Redis does not scale.
- data size dictates the max throughput we can get out of Redis (And network as well)
- several hundread thousand per second load may not work on a single cluster. Multuple clusters are needed.
In this framework, several optimisation are used:
- Each file invokes a cloud function to process it. (via triggers on gcs buckets)
- Each cloud function devides the incoming files into chunks of certain size to process it.
- Each cloud function uses multiple threads to process file chunks in parallel.
- Redis connection pooling is used to avoid creating connections on the fly.
- Redis pipeline is used to batch writes and reads together.
- Consistent hashing is used to distribute load on multiple Redis Clusters.
- Memoerystore Redis' write and read endpoint are used.
- Writes are only sent to the write endpoint
- Reads are sent to read endpoint which in turn takes care of balacing it across available read replicas.